【科普】碳中和技术与前景
1. 可再生能源技术
Technologies for renewable energy
对标碳中和,实现一次能源有序减量替代,需大力发展可再生能源。可再生能源是一个完整的技术体系,不仅需要太阳能、风能、地热能、海洋能等,更需要储能技术的配合,形成真正的新能源体系。核能与氢能具有清洁低碳、绿色环保等优点,是实现碳中和目标的重要技术;生物质能也是实现能源结构调整的重要支撑。本文总结了可再生能源大规模应用中的关键核心技术,以及这些关键核心技术对实现碳中和目标的影响,同时对这些技术未来的发展进行了展望(图2)。
Achieving C neutrality requires replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources. Harnessing the power of solar, wind, geothermal, ocean, nuclear, and H 2 energy may help secure global energy security without relying on fossil fuels. Bioenergy is also important in reshaping the energy supply and consumption systems. Technologies for these renewable energy sources and their future development are discussed (Fig. 2).
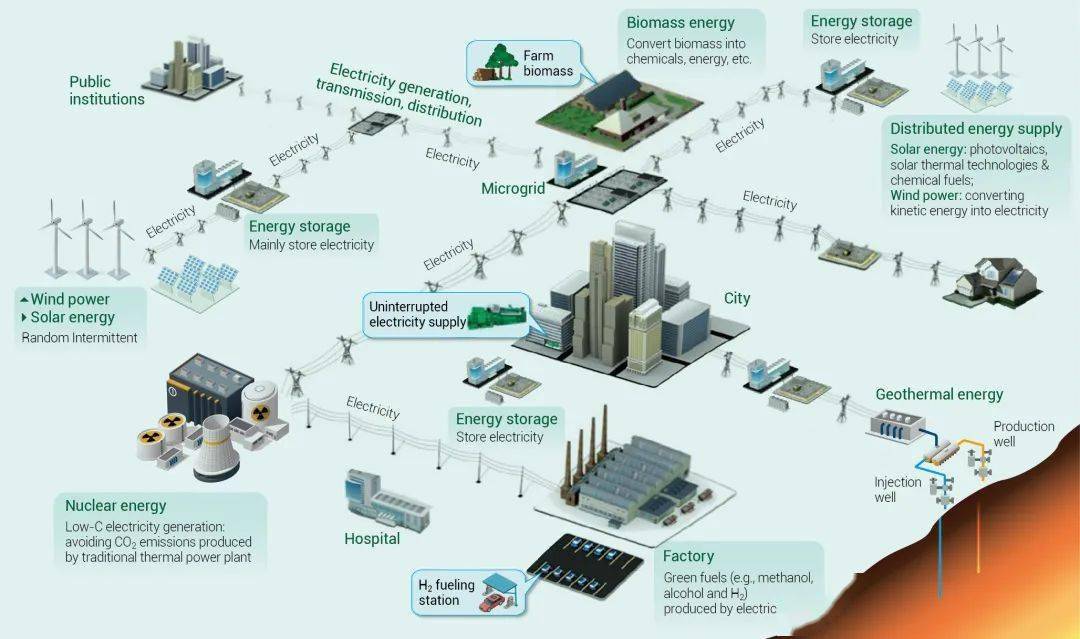
图2 可再生能源技术
Fig. 2 Technologies for renewable energy
2. 增强全球生态系统碳汇技术
Technologies for enhancing C sink in global ecosystems
为实现全球生态系统碳中和,迫切需要减少农业食物源温室气体排放和提高生物圈的碳固持量(图3)。选育优良作物和家畜品种,农田精准灌溉、施肥与土壤增碳,优化家畜饲养和粪便管理,变革基于土地利用的动植食物生产等措施,以减少农业食物源温室气体排放;实施可持续管理森林草地生态系统,增强岩石风化作用和采用生物炭技术等措施提高陆地生态碳汇;通过保护滨海湿地与海洋生态系统,实施可持续海水养殖、人工涌升流和陆海一体化战略,提升海洋生态系统碳汇能力。
Global agricultural food systems are the major source of global anthropogenic GHG emissions, while terrestrial and marine ecosystems are the most important global C sinks (Fig. 3). To avoid disastrous climate change, global ecosystems need to be reformed to increase C sequestration, biomass production, and food supply while lowering GHG emissions.
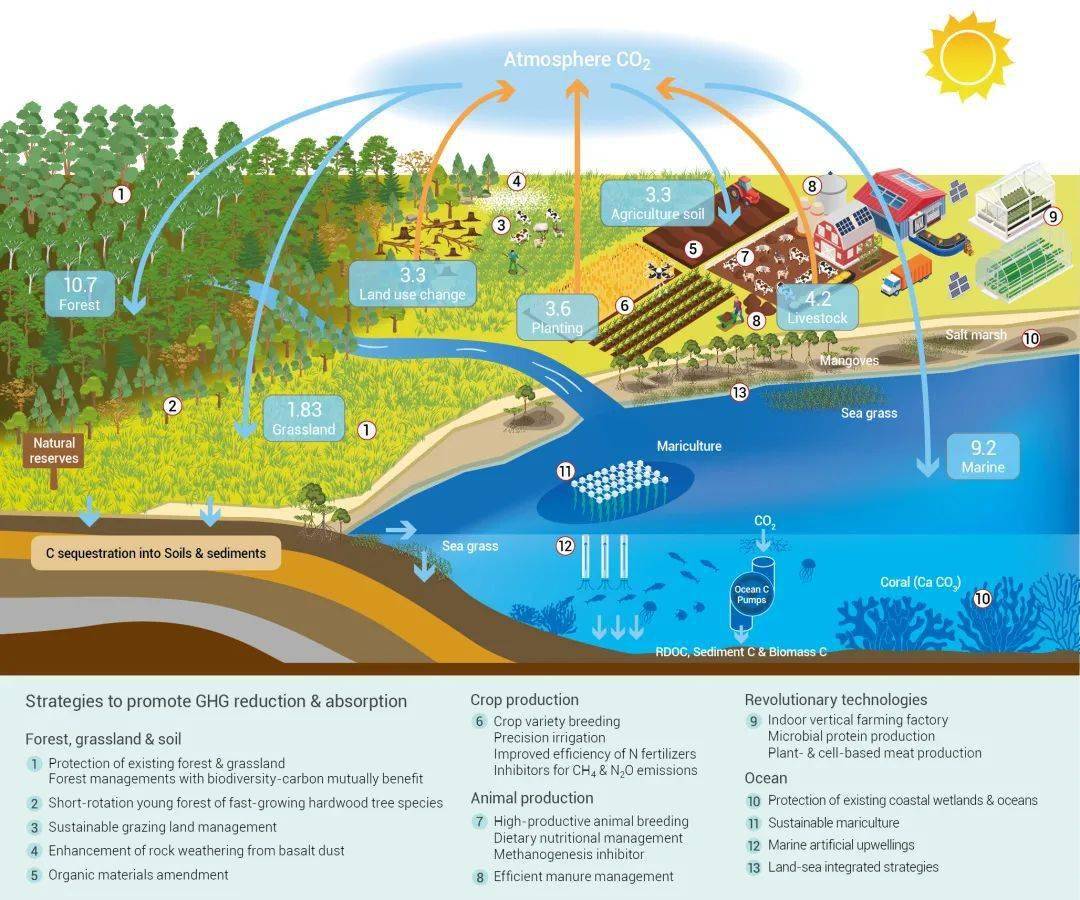
图3 全球生态系统温室气体流通量、减排和吸收策略
Fig. 3 Overview of global GHG budget and strategies to promote GHG reduction and sequestration in global ecosystems
3. 解决全球废弃物碳足迹问题
Tackling the C footprint of global waste
作为减少全球废弃物碳足迹的有效策略, 将固体废弃物转化为生物炭,能够减少温室气体排放,实现碳封存,有利于促进循环经济发展。大量有机废弃物,如植物残体、牲畜粪便、厨余垃圾、工业生物垃圾、动物尸体等,都可制备生物炭。生物质炭可用于土壤改良、环境修复、化学品生产、建筑材料和饲料配方(图4)。
As an effective strategy to reduce the C footprint of global waste, thermochemical conversion of solid waste into biochar can bring multifunctional benefits to the circular economy in addition to climate change mitigation and C sequestration.A plethora of organic resources, such as crop residues, forest residues, livestock manure, food wastes, industrial biowastes, municipal biowastes, animal carcasses, are feedstocks that can be used to produce biochar for different purposes. Biochar is used in a variety of applications, including soil amendment, delivery of agrochemicals and microbes, environmental remediation, catalyst production, building material manufacturing, and feed formulation (Fig. 4).
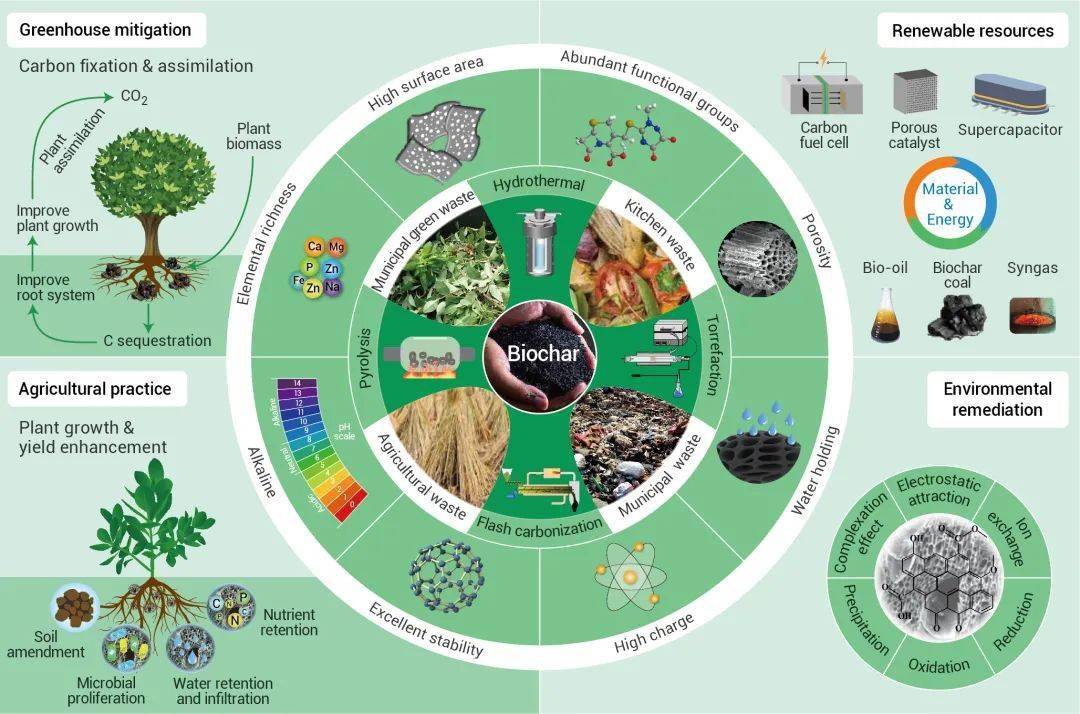
图4 零废弃生物炭作为可持续发展的碳中和工具
Fig. 4 Zero waste biochar as a C-neutral tool for sustainable development
4. 碳捕集、利用和储存的技术
Technologies for C capture, utilization, and storage
CCUS是捕集、利用和储存CO 2 的技术,对实现碳中和至关重要。 CCUS需要技术创新以实现低成本和近零能耗捕集,同时实现碳封存与地下资源开采协同和风险管理技术。未来的突破方向:化学链燃烧、多联产、化石能源和可再生能源互补捕集CO 2 等技术。CO 2 转化为燃料或者化工品也是碳减排的重要途径(图5)。
CCUS, technologies for carbon capture, utilization, and storage, are critical to achieving C neutrality (Fig. 5). CCUS technologies need innovations, targeting CO 2 recovery with low energy or even zero energy penalty, and aiming collaborative optimization of CO 2 storage and resource recovery and risk management . Chemicals-power polygeneration and chemical looping combustion with CO 2 capture have the potentials to realize low-cost CO2 capture. Fossil fuels combined with renewable energy for CO2 capture, the complementary energy systems, may play an important role for future CCUS. The conversion of CO2 into fuels and chemicals is a promising direction for C reduction.
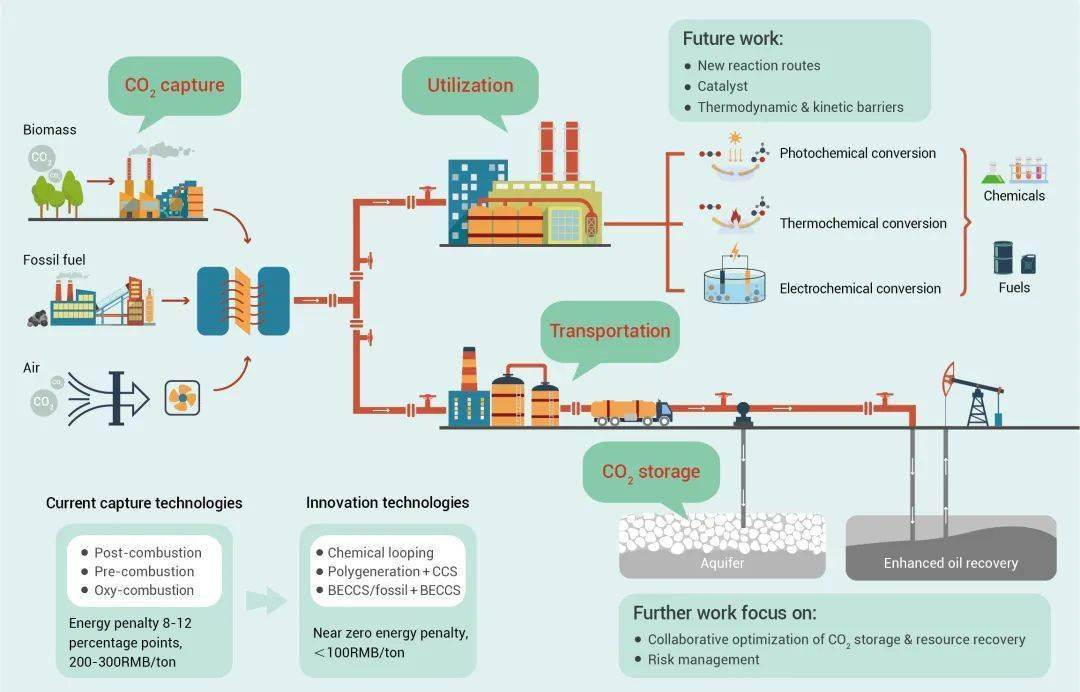
图5 工业体系二氧化碳捕集技术发展的路线图
Fig. 5 The roadmap for CO 2 capture technology development in the industry
5. 卫星对地观测与数字地球技术
C neutrality based on satellite observations and digital earth
卫星对地观测和数字地球技术是空天地一体监测碳循环的重要手段,能为碳中和研究提供高时空分辨率的基础观测数据和分析工具。碳卫星、多光谱卫星为监测温室气体浓度提供数据支撑;数字地球技术综合全球植被、大气、气候数据,为自然生态系统碳收支提供时空分析与可视化展示。
Satellite observation and digital earth technology are important parts of monitoring C emissions and establishing an air-space-ground integrated observation system for the C cycle. They can provide basic observation and analysis data with a high temporal and spatial resolution for C neutralization research. C satellite and multispectral satellites can provide data support for monitoring the concentration of greenhouse gases; digital earth technology can integrate global vegetation, atmosphere, and climate data to provide temporal and spatial analysis of the C budget of natural ecosystems.
总结与展望 | Conclusions & perspectives
世界正朝着碳中和迈进,未来需构建以清洁能源为主体的新型电力系统,实现一次能源有序减量替代和可再生能源的大规模应用;统筹生态系统保护和固碳功能,推进基于土地利用与食物生产变革,提高陆海一体生态碳汇;优化生物炭生产和生命周期过程,制定标准推进低碳产业发展;利用多联产技术、化学链燃烧技术、化石燃料与可再生能源互补技术,解决CCUS技术推广高能耗高成本障碍;发展新型卫星,全面监测温室气体排放和陆海碳汇,星地协同增强碳收支核算能力。全球须通力合作、技术共享,以早日实现碳中和与可持续发展。
As the world races towards C neutrality, it is critical to revise current global C fluxes. To meet the climate change mitigation goals by the middle century, all people including investors, researchers, policy makers and consumers must work together:
(1) To realize orderly reduction and replacement of fossil fuel energy sources with renewable energy sources, we need to vigorously develop energy storage systems to address the intermittency of renewable energy sources. (2) To coordinate ecosystem protection and carbon sequestration, we need to push forward reform of crop-livestock production systems based on land use and improving ecological carbon sink. (3) To integrate ecological strategies optimizing biochar production, life cycle analysis, and formulate standards to advance the development of green and low-carbon industries. (4) To adopt breakthrough CCUS technologies including polygeneration, chemical looping combustion, and fossil fuels combined with renewable energy for CO 2 capture, to overcome the high energy consumption and high costs. (5) To develop new satellites to comprehensively and timely monitor GHG emissions, and to expand the ability to calculate C budgets through joint observation from space and the ground.


